Society depends on reliable and resilient energy to maintain essential functions. With an increase in natural and manmade threats, power and energy systems remain vulnerable to hazards.
The societal impacts of hazardous weather events and climate change are ever increasing. The resilience of critical infrastructure to face, for example, the challenges posed by wildfires and hurricanes is being tested around the globe. The effects of climate change require sustained planning to deal with the complex interactions between environmental conditions, critical infrastructure and human health.
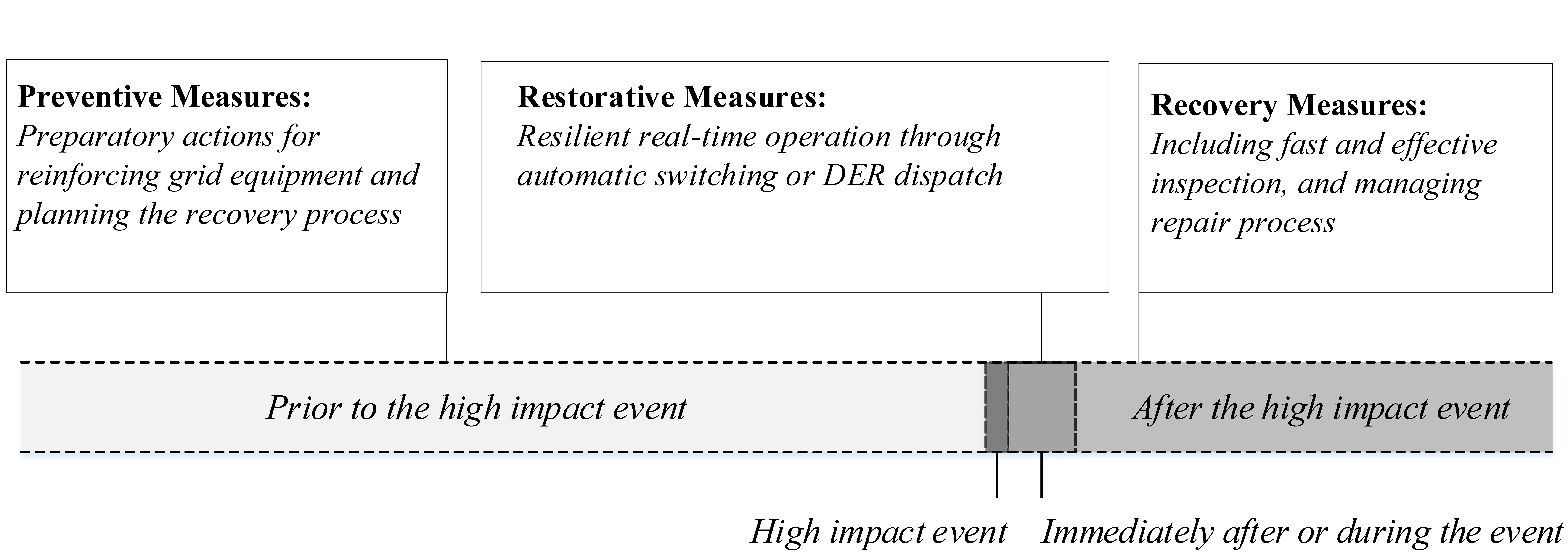
Our research develops models and tools to assess and enhance the resilience of power and energy systems and interdependent critical infrastructure against a multitude of natural disasters that cause large-scale interruption on critical services.
We develop models to reduce the impacts of natural disasters (preventive/preparatory models), as well as to restore and recover the system after outages.